When the Network Discovery method is used in Configuration Manager 2007, and the Topology option is selected, only routers and subnets are discovered and stored in the Configuration Manager site database.
In general, how extensive this discovery is depends largely on the number of router hops you select for the Network Discovery run. A hop is the passing of data between two network nodes, so increasing the number of hops will dramatically increase the extent of the discovery.
For example, a topology-only discovery with 0 router hops will discover the subnet on which the originating server resides, up to and including any router that it encounters. A topology-only discovery with 1 router hop will discover that same subnet and router, any subnets linked to that first router, and routers on those subnets.
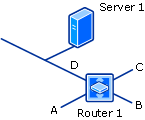
The following diagram shows what this type of Network Discovery finds when it runs on Server 1 with 0 router hops specified: subnet D and Router 1.
For additional information on how router hops have an impact on Network Discovery, see About Router Hops in Network Discovery.