The following planning activities help ensure the success of the Operations Review.
Selecting the Review Team Lead
The individual in charge of the review is the operations manager, who comes from the Operations Role Cluster in the Microsoft Operations Framework (MOF) Team Model.
Team Lead Sets Review Parameters
The team lead is responsible for identifying who should attend the Operations Review and setting the review date, time, location, technology, and review scope.
Mandatory Attendees
The team lead selects the review team members. Attendees of the Operations Review must be of the right level in order to ensure that the meeting and actions that result from it are put into effect. If the attendees are not at a management level, they need to have management support at a high level to reinforce their actions. This management support prevents other work from receiving a higher priority than the delivery of improvements to the service.
The key stakeholders and decision makers in the Operations Review meeting are:
- The IT operations management team.
- The service managers whom are responsible for the services
being delivered.
The service managers remain the primary interface between IT and the rest of the business and are held accountable by the business for the delivery of IT services. This means that they are the customers of the operations team and should be involved and treated as such.
The IT operations organization is normally structured according to the technology or platform being supported, including the following teams:
- Network administration team.
- Server administration team.
- Directory services administration team.
- Messaging administration team.
- Database management administration team.
- Other technology administration teams.
Additional systems management-related teams are in place to provide the functional support needed to maintain and manage the technology, including the following teams:
- Event monitoring team (also known as a bridge or command
center).
- Storage management, backup, and recovery team.
- Workload, output management, and scheduling team.
- Security administration team.
Each support team should be represented by the most senior team member, normally the line manager, at the Operations Review. Each team will be expected to review its own team's performance and contribution and to provide suggested improvement actions where service levels are not achieving the desired levels.
Optional Attendees
The MOF Team Model organizes the activities of IT operations into seven distinct role clusters that represent functional roles. Since Operations represents only one of the seven role clusters, we recommend that the review be attended by senior members of the other MOF Team Model role clusters. For example, the Supporting Role Cluster will have valuable input in terms of the major incidents that have occurred in the previous measurement period and what impact they have had on the business (both the actual service impact and the perceived service impact to the end-users). More information on team roles is available in the MOF Team Model for Operations document, available at the Microsoft Operations Framework (MOF).
The following figure depicts the MOF Team Model role clusters and their associated functional roles:
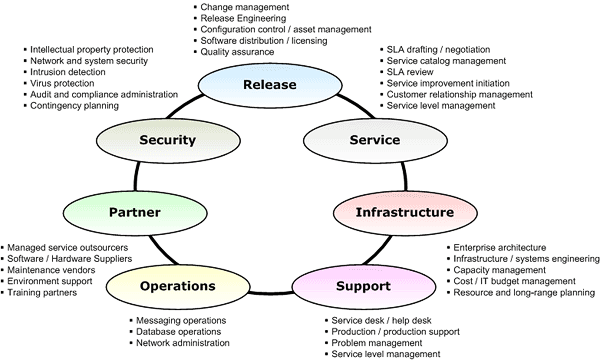
The Operations Review is an internal meeting, and it is not standard practice to invite any outside participants to it. This is because internal performance measurements, including financial and human resource indicators, are typically reviewed. It is acknowledged that many IT organizations do make use of third parties to deliver some of the services; separate regular performance reviews should be held with those parties prior to the scheduled Operations Review, and any pertinent issues or decisions made should be communicated to the forum in attendance at the Operations Review.
In some instances, the relationship between the third party and IT operations may be very mature and longstanding. In such cases, the business will accept the risk of having a third party attend because of the value that will be added to the meeting.
Other Review Parameters
Also, during this step, the Operations Review team lead:
- Sets the date, time, nature, and length of the Operations
Review meeting.
- Selects and reserves the meeting technology and location, such
as the physical meeting location, video conferencing, Microsoft
NetMeeting conferencing software, teleconferencing, or some
combination thereof. The team lead also obtains meeting supplies
and equipment, such as a PC projection system and
flipcharts.
- Sets the scope of the review, that is, which operational levels
will be reviewed, which may be a subset of operational levels
associated with the service solution. Criteria for choosing which
operational levels are to be reviewed include:
- Those that have not been consistently delivered to service or
operational levels.
- Those that have required significantly more effort or
investment to operate than planned.
- Those where significant changes in the environment or the
service solution itself have occurred or are anticipated.
- Those with significant impact on service or operating level
achievement, on the business, or on customers and users.
- Those with significant impact of service or operational level
delivery on the IT environment (organization and
infrastructure).
- Those that have not been consistently delivered to service or
operational levels.
- Reviews "lessons learned," minutes, and action plans from
previous Operations Reviews of the service solution or similar
service solutions with particular attention paid to:
- The status of committed action items from previous reviews of
the service solution.
- Trends in previous reviews.
- The status of committed action items from previous reviews of
the service solution.
Team Lead Sets Review Agenda
A written agenda often improves the effectiveness of a meeting. In this step, the review team lead modifies the agenda template where necessary, ensures that participants understand their particular roles in the meeting, and assigns facilitative roles (such as minute-taker and timekeeper).
The team lead should communicate the agenda well in advance to help attendees prepare for the meeting, allowing for optimized discussions during the review. Further information on what the agenda should include is contained in the Meeting Agenda section later in this document. Also you can access an online template version of the sample agenda at Operations Templates.
Team Lead Announces Meeting Details
In this step, the review team lead sends the meeting information to all review team members. This information includes:
- The review definition template that outlines basic review
parameters. For a complete set of templates available online, see
Operations Templates.
- The meeting agenda.